Urolithin A vs Fisetin: Which is Superior for Longevity?
Urolithin A and fisetin are two healthy compounds that work in different ways. Read to explore Urolithin A vs fisetin and the benefits of each.
What to know
Fisetin and Urolithin A are two healthy compounds that work in different ways.
Urolithin A supports mitochondrial and muscle health, while fisetin helps clear out senescent cells that contribute to aging.
Fisetin is found in fruits like strawberries, while Urolithin A is made by your gut microbiome.
Urolithin A has more human studies on its effectiveness for muscle strength, energy, and aging, while fisetin’s research is still emerging.
Urolithin A vs Fisetin: How To Choose
With interest in longevity at an all-time high, a new wave of supplements promising cellular renewal and healthy aging is gaining traction. Urolithin A and fisetin are two standout contenders.
Urolithin A is a postbiotic compound produced in the gut when certain microbes metabolize polyphenols found in pomegranates and other fruits. It’s best known for its role in supporting mitochondrial health through a process called mitophagy, the cellular cleanup that helps remove damaged mitochondria and promote energy production.
Fisetin, on the other hand, is a naturally occurring plant compound found in various fruits and vegetables. It is considered a flavonoid, a plant ingredient gaining attention for its potential health benefits. In particular, it appears to play a role in clearing out senescent cells.
As interest in longevity research grows, these two supplements are gaining popularity. While fisetin is marketed for its potential to support healthy aging, brain function, and cellular health, does the science match the claims? And how does it compare to the clinical data behind Urolithin A?
This article explores the difference between Urolithin A vs fisetin, how they compare, and which may be a better choice based on your goals.
What is Fisetin?
Fisetin is a natural compound found in fruits and vegetables like strawberries, apples, persimmons, grapes, onions, and cucumbers that holds the potential to support longevity.[1] Since it’s only present in small amounts in these foods, many people turn to fisetin supplements for a more concentrated dose.
Fisetin supports healthy aging differently than Urolithin A. Instead of directly targeting mitochondrial health, like Urolithin A, fisetin targets zombie cells, cells that are dysfunctional but don’t die. These cells no longer function properly and thus can contribute to inflammation and, subsequently, disease.[2]
To produce its benefits, fisetin acts as an antioxidant to protect cells from oxidative stress and inflammation.[3]
By targeting the hallmarks of aging, fisetin, like Urolithin A, may contribute to longevity and overall well-being.
Potential Fisetin Benefits
Fisetin is known for its ability to clear out aging or damaged cells. As an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compound, fisetin may benefit several aspects of health and may play a part in suppressing tumor growth, protecting nerve cells, and more.
It’s important to note that the majority of fisetin studies are preclinical, meaning they are in animals or cell cultures. Until more human clinical trials have been completed, we cannot assume that the benefits in the existing literature will extend to humans.
May protect nerve cells
Animal models have shown that fisetin may protect the brain by protecting nerve cells from damage and degeneration.[4] Because fisetin acts as an antioxidant, it can protect the cells, including nerve cells in the brain, from oxidative stress.[5]
May support immune function
Preclinical studies show that fisetin can trigger immune system responses to attack foreign invaders.[6] It can also inhibit the expression of pro-inflammatory compounds that can lead to illness.
May promote heart health
Fisetin may also support the heart by keeping the cells in your blood vessels healthy and well-functioning. In mice studies, supplementing with fisetin was seen to reduce cell senescence in the cardiovascular system and improve blood flow and vascular function.[7]
Optimal blood flow can support healthy blood pressure and reduce the risk of plaque build-up in the arteries.[8]
Optimal Fisetin Dosage
Since human studies with fisetin are limited, it is hard to determine the best fisetin dosage. Based on mouse studies, we can assume that the human dose equivalent might be around 500 mg/day to see benefits.[9]
However, most fisetin supplements provide only a fraction of this amount, typically between 40 and 100 mg per serving. So you may be wondering, “Is fisetin worth it?” and this answer needs to be investigated with future research studies.
How to Take Fisetin
Fisetin is fat-soluble, and it has low bioavailability. For this reason, most manufacturers recommend taking fisetin with a meal that contains fat.
Fisetin Side Effects
Fisetin is generally considered safe and well tolerated by most people when consumed from food. However, fisetin supplement side effects have been reported, specifically gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.[10]
In addition, fisetin may interact with blood thinners and increase the risk of bleeding. Animal studies have shown that fisetin may also have estrogen-like activity, which means it can act similarly to estrogen in the body. This estrogen-like activity can pose a potential risk or interaction for those with hormone-sensitive conditions such as breast cancer. [11]
Because of these possible side effects, those taking blood thinners such as Warfarin or those with hormone-related conditions should speak to their doctor before taking fisetin supplements.
About Urolithin A
Urolithin A is a postbiotic produced in the gut upon digestion of certain foods like pomegranates, berries, and nuts. Since it is a postbiotic, it is considered a byproduct of food digestion and is not a nutrient directly found in food itself. Therefore, there are no foods high in Urolithin A; rather, there are foods high in the dietary precursors.
Clinical trials with Urolithin A have demonstrated benefits for muscle health, immune health and skin health, stimulating mitophagy, the essential process for recycling and renewing damaged mitochondria. This process is a non-negotiable for healthy aging and energy preservation throughout life.[12]
The challenge is that while Urolithin A can be produced via digestion, research shows a large majority of the population doesn’t have the right gut microbiome to be a “producer.”[13][𝑛] Even those who can produce it would need to drink at least six cups of pomegranate juice to get a benefit similar to a 500mg daily supplement.
Because of this, a direct dose of Urolithin A via supplementation is the most efficient way to take in this powerhouse nutrient.
Urolithin A Benefits
Urolithin A is supported by over 15 years of research, including several well-conducted human clinical trials. This research shows its ability to support mitochondrial health, muscle function, and skin health, and to target key aging pathways.[14]
Urolithin A benefits the body by stimulating mitophagy, the mitochondrial recycling process that clears out defective mitochondria, keeping our cells healthy and less prone to aging.[15]
Mitopure®, the first clinically validated Urolithin A supplement, has been used in over 11 human clinical trials, making it one of the most studied longevity supplements on the market.
Supports muscle health
Whether you’re an elite athlete, recreational exerciser, or someone with little to no exercise, combating age-related muscle loss is key to improving overall longevity. By supporting cellular energy production, Urolithin A has the potential to improve both muscle strength and endurance.
Clinical trials with Mitopure have shown:
- 12% increase in muscle strength after 16 weeks when taking a 500mg dose
- 17% improvement in muscle endurance after 8 weeks when taking a 1000mg dose
Improves skin health
Topical application of Mitopure (Urolithin A) targets both the biological and external factors that lead to skin aging.
When topically applied, research has shown that Mitopure:[16]
- Slows intrinsic skin aging, the internal, driven biological processes that cause skin to age.
- Protect against extrinsic aging. External factors, including UV damage, are the primary cause of skin aging.
- Reduce wrinkle depth and appearance. An 8-week clinical trial found that daily application of Mitopure significantly reduced wrinkle depth and volume compared to the placebo.
- Supports collagen assembly. With age, collagen-associated genes experience downregulation. Mitopure was found to significantly upregulate these genes, promoting collagen organization and skin resilience.
Supports immune health
Clinical studies suggest that taking 1000mg of Mitopure daily for 1 month can improve several markers of immune health in healthy adults.

Optimal Mitopure Dose
The recommended daily dose of Urolithin A is 500 to 1000 mg. Mitopure is now available in softgel, powder, and gummy forms to fit seamlessly into your lifestyle.

Mitopure Gummies
4.7 · 885 reviews
A strawberry-flavored dose of cellular energy
How to Take Mitopure Supplements
Urolithin A can be taken at any time of day, with or without food. Check out our Mitopure User Guide for a more detailed explanation on the best ways to incorporate Mitopure into your daily routine.
How to Use Timeline’s Skincare Line
If you are looking for the benefits of topically applied Mitopure, Timeline has four products in their skin care line:
- The Serum: Apply first to clean, dry skin daily. The Serum can be used day and night.
- The Day Cream: Apply during the day, under sunblock.
- The Night Cream: Apply at night to clean, dry skin.
- The Eye Cream: Apply day and night to the delicate skin around the eye.
Urolithin A Side Effects
Urolithin A has a strong safety profile, with no reports of serious side effects or adverse effects in doses up to 1000 mg per day.[17]
Urolithin A vs Fisetin: A Comparison
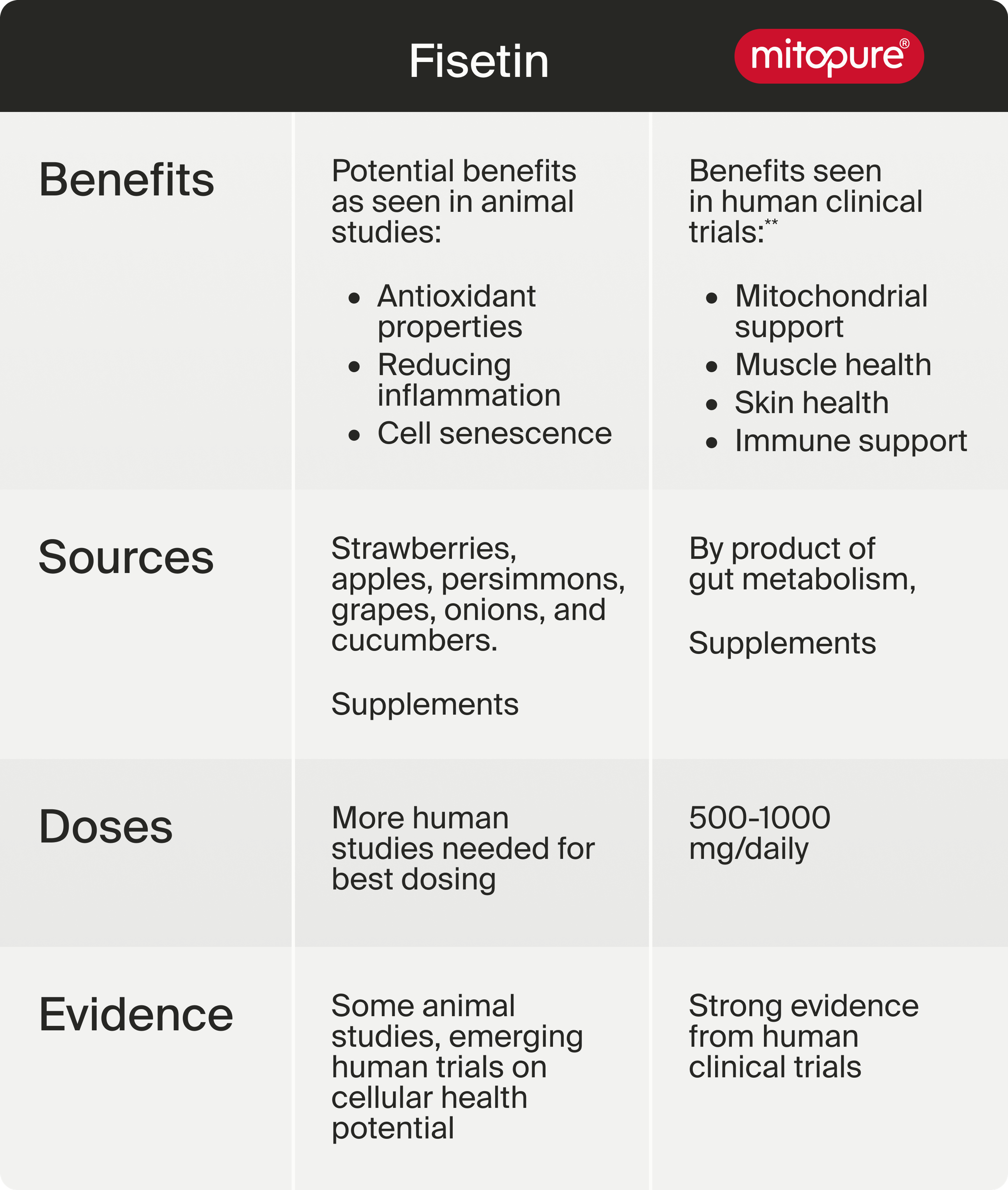
Who Should Take What?
While the research for both molecules is promising, Mitopure (Urolithin A) has far more human-level data to support both its safety and efficacy. To truly understand how fisetin can support human health, more clinical trials will be needed; however, the benefits of Mitoupre for humans are robust and continue to grow.
Regardless of what you choose, make sure to always speak to your physician before starting a new supplement regimen.

Food vs. Supplement Debate - Can I Get This Naturally from Food?
For both fisetin vs Urolithin A, you would likely need to take them in supplement form to get enough.
Strawberries are one of the most abundant sources of fisetin, but it’s unclear how many strawberries you’d need to eat to get enough fisetin, as there is no standard dose. However, strawberries and other foods high in fisetin are still nutritious foods with many benefits and can be incorporated into a healthy diet to potentially reap some fisetin benefits.
Most people don’t have the right gut microbiome to make Urolitin A, making diet a challenge to get enough of this molecule.[18] And, even if you can produce it, you’d need to drink six cups of sugary pomegranate juice daily to get enough. You’re best bet is to take it in a clinically validated supplement form, such Mitopure.
Final Words
While both fisetin and Urolithin A target biological hallmarks of aging, they do so in different ways. Fisetin helps remove senescent cells, while Urolithin A supports mitochondrial health.
However, it's important to note that Urolithin A has more human research backing its benefits, making it a superior choice in terms of known benefits and safety. While fisetin shows promise in cellular health, the research is still in the early stages. If you're looking for a well-researched supplement with proven effects on energy and longevity, Urolithin A, the active ingredient in Mitopure, stands out.
Authors

Written by
Dietitian-Nutritionist, and Health Content Writer

Reviewed by
Director Science Communications
References
- ↑
Shen J, Shan J, Zhong L, et al. Dietary Phytochemicals that Can Extend Longevity by Regulation of Metabolism. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2022;77(1):12-19. doi:10.1007/s11130-021-00946-z
- ↑
Freund, A., Orjalo, A., Desprez, P., & Campisi, J. (2010). Inflammatory networks during cellular senescence: causes and consequences.. Trends in molecular medicine, 16 5, 238-46 . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2010.03.003 (https://www.google.com/url?q=https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2010.03.003&sa=D&source=docs&ust=1746802866779129&usg=AOvVaw2CyhZESXeu1384245Wpd3b).
- ↑
Hassan, S., Samanta, S., Dash, R., Karpiński, T., Habibi, E., Sadiq, A., Ahmadi, A., & Bungău, S. (2022). The neuroprotective effects of fisetin, a natural flavonoid in neurodegenerative diseases: Focus on the role of oxidative stress. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.1015835 (https://www.google.com/url?q=https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.1015835&sa=D&source=docs&ust=1746802866781301&usg=AOvVaw2XJoovpkmmQM88G0Gv3W3J).
- ↑
Elsallabi O, Patruno A, Pesce M, Cataldi A, Carradori S, Gallorini M. Fisetin as a Senotherapeutic Agent: Biopharmaceutical Properties and Crosstalk between Cell Senescence and Neuroprotection. Molecules. 2022;27(3):738. Published 2022 Jan 23. doi:10.3390/molecules27030738
- ↑
Jiang Y, Tang X, Deng P, et al. The Neuroprotective Role of Fisetin in Different Neurological Diseases: a Systematic Review. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(11):6383-6394. doi:10.1007/s12035-023-03469-7
- ↑
Elsallabi O, Patruno A, Pesce M, Cataldi A, Carradori S, Gallorini M. Fisetin as a Senotherapeutic Agent: Biopharmaceutical Properties and Crosstalk between Cell Senescence and Neuroprotection. Molecules. 2022;27(3):738. Published 2022 Jan 23. doi:10.3390/molecules27030738
- ↑
Prem P, Sivakumar B, Sri Rahavi Boovarahan, Kurian GA. Recent advances in potential of Fisetin in the management of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury–A systematic review. Phytomedicine. 2022;101:154123-154123. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154123
- ↑
Mahoney SA, Venkatasubramanian R, Darrah MA, et al. Intermittent supplementation with fisetin improves arterial function in old mice by decreasing cellular senescence. Aging Cell. 2024;23(3):e14060. doi:10.1111/acel.14060
- ↑
Elsallabi O, Patruno A, Pesce M, Cataldi A, Carradori S, Gallorini M. Fisetin as a Senotherapeutic Agent: Biopharmaceutical Properties and Crosstalk between Cell Senescence and Neuroprotection. Molecules. 2022;27(3):738. Published 2022 Jan 23. doi:10.3390/molecules27030738
- ↑
Shivani Malviya, Arpana Parihar, Dipesh Singh Parihar, Khan R. Natural products as a therapy to combat against SARS-CoV-2 virus infection. Elsevier eBooks. Published online January 1, 2022:115-145. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-323-91172-6.00017-0
- ↑
Shivani Malviya, Arpana Parihar, Dipesh Singh Parihar, Khan R. Natural products as a therapy to combat against SARS-CoV-2 virus infection. Elsevier eBooks. Published online January 1, 2022:115-145. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-323-91172-6.00017-0
- ↑
Faitg J, D'Amico D, Rinsch C, Singh A. Mitophagy Activation by Urolithin A to Target Muscle Aging. Calcif Tissue Int. 2024;114(1):53-59. doi:10.1007/s00223-023-01145-5
- ↑
- Singh A, D'Amico D, Andreux PA, et al. Direct supplementation with Urolithin A overcomes limitations of dietary exposure and gut microbiome variability in healthy adults to achieve consistent levels across the population. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2022;76(2):297-308. doi:10.1038/s41430-021-00950-1
- ↑
Liu S, D’Amico D, Shankland E, et al. Effect of Urolithin A Supplementation on Muscle Endurance and Mitochondrial Health in Older Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(1):e2144279. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.44279
- ↑
Liu S, D’Amico D, Shankland E, et al. Effect of Urolithin A Supplementation on Muscle Endurance and Mitochondrial Health in Older Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(1):e2144279. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.44279
- ↑
Singh A, D'Amico D, Andreux PA, Fouassier AM, Blanco-Bose W, Evans M, Aebischer P, Auwerx J, Rinsch C. Urolithin A improves muscle strength, exercise performance, and biomarkers of mitochondrial health in a randomized trial in middle-aged adults. Cell Rep Med. 2022 May 17;3(5):100633. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100633. PMID: 35584623; PMCID: PMC9133463.
- ↑
Singh A, D’Amico D, Andreux PA, et al. Urolithin A improves muscle strength, exercise performance, and biomarkers of mitochondrial health in a randomized trial in middle-aged adults. Cell Reports Medicine. 2022;3(5):100633. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100633
- ↑
Singh, A., D’Amico, D., Andreux, P.A. et al. Direct supplementation with Urolithin A overcomes limitations of dietary exposure and gut microbiome variability in healthy adults to achieve consistent levels across the population. Eur J Clin Nutr 76, 297–308 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-021-00950-1